52 Years of Fiat: The economic legacy of abandoning the gold standard

Introduction
In 1971, the United States abandoned the gold standard, a monetary system that had been in place since the late 19th century. This decision had far-reaching consequences for the global economy, and its effects are still being felt today, more than five decades later. In this article, we will explore the economic legacy of fiat currency and how it has affected the world.
What is Fiat Currency?
Fiat currency is a type of money that is not backed by a physical commodity such as gold or silver. Instead, it is backed by the government that issues it. Fiat currency has value only because the government says it does. This is in contrast to commodity-based currencies, which have intrinsic value because they are made of a valuable material.
The Gold Standard
Before the adoption of fiat currency, many countries used the gold standard. Under this system, a country's currency was backed by gold reserves held by its central bank. This meant that the government could only print as much money as it had gold reserves to back it up. The gold standard was seen as a way to limit inflation and stabilize the value of a country's currency.
Why Was the Gold Standard Abandoned?
The gold standard was abandoned for several reasons. One of the main reasons was the need for governments to print more money to finance their spending. With a gold-backed currency, governments could only print as much money as they had gold reserves to back it up. This meant that if they wanted to spend more money than they had in reserves, they would have to either raise taxes or borrow money.
Another reason for abandoning the gold standard was to allow for greater flexibility in monetary policy. Under a gold-backed currency, a country's central bank could not easily adjust interest rates or engage in other monetary policies to stimulate the economy. With fiat currency, central banks have greater control over monetary policy.
The Economic Legacy of Fiat Currency
Since the adoption of fiat currency, there have been both positive and negative economic consequences. On the positive side, fiat currency has allowed governments to finance their spending more easily. This has enabled them to invest in infrastructure, education, and other areas that can stimulate economic growth.
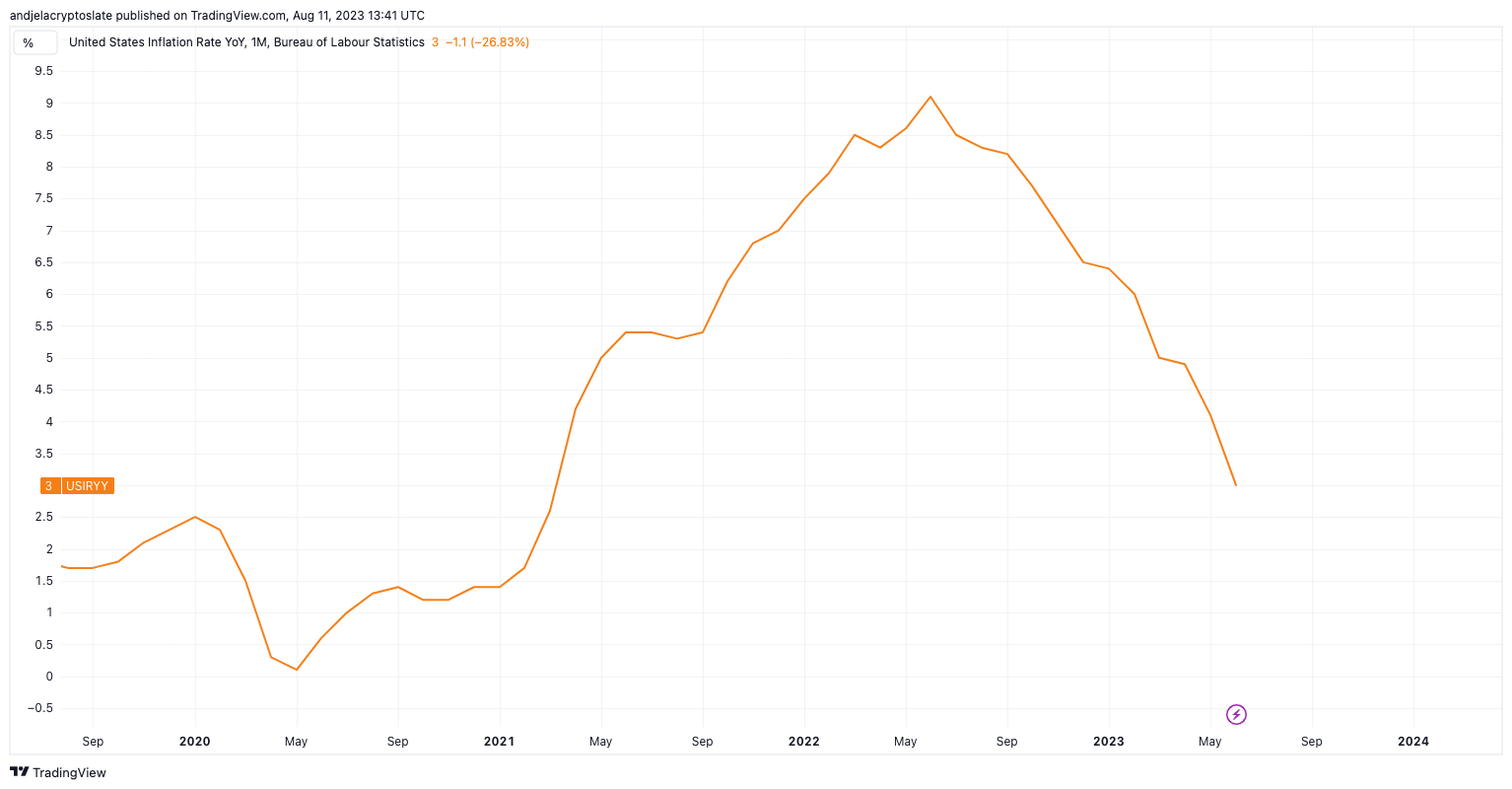
However, there have also been negative consequences. One of the most significant is inflation. Because fiat currency is not backed by a physical commodity, governments can print as much money as they want without limit. This can lead to an increase in the money supply, which can cause prices to rise.
Another negative consequence of fiat currency is that it can lead to a loss of confidence in the currency itself. If people do not believe that a currency has value, they may be less willing to use it. This can lead to a decrease in demand for the currency, which can cause its value to fall.
Conclusion
The decision to abandon the gold standard and adopt fiat currency has had far-reaching consequences for the global economy. While it has allowed governments greater flexibility in monetary policy and enabled them to finance their spending more easily, it has also led to inflation and a loss of confidence in currencies. As we look to the future, it is important to consider these consequences and work towards solutions that can help mitigate them.