Bitcoin circling the $30,000 mark nine months ahead of next halving
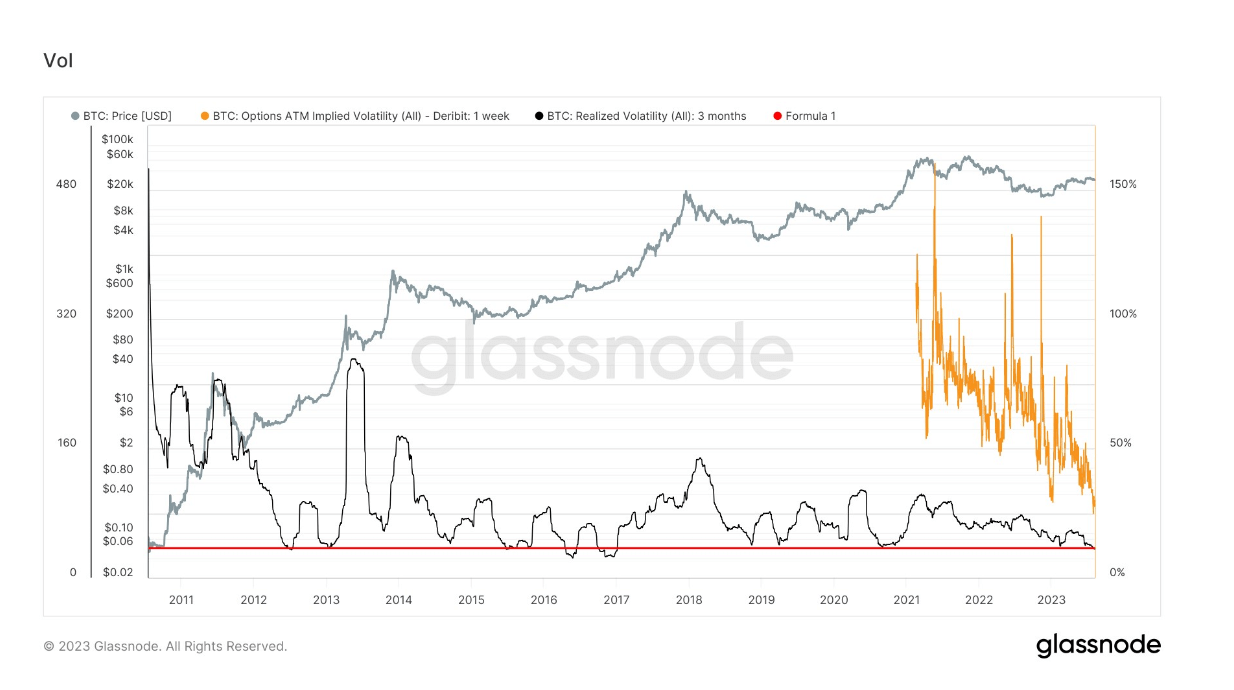
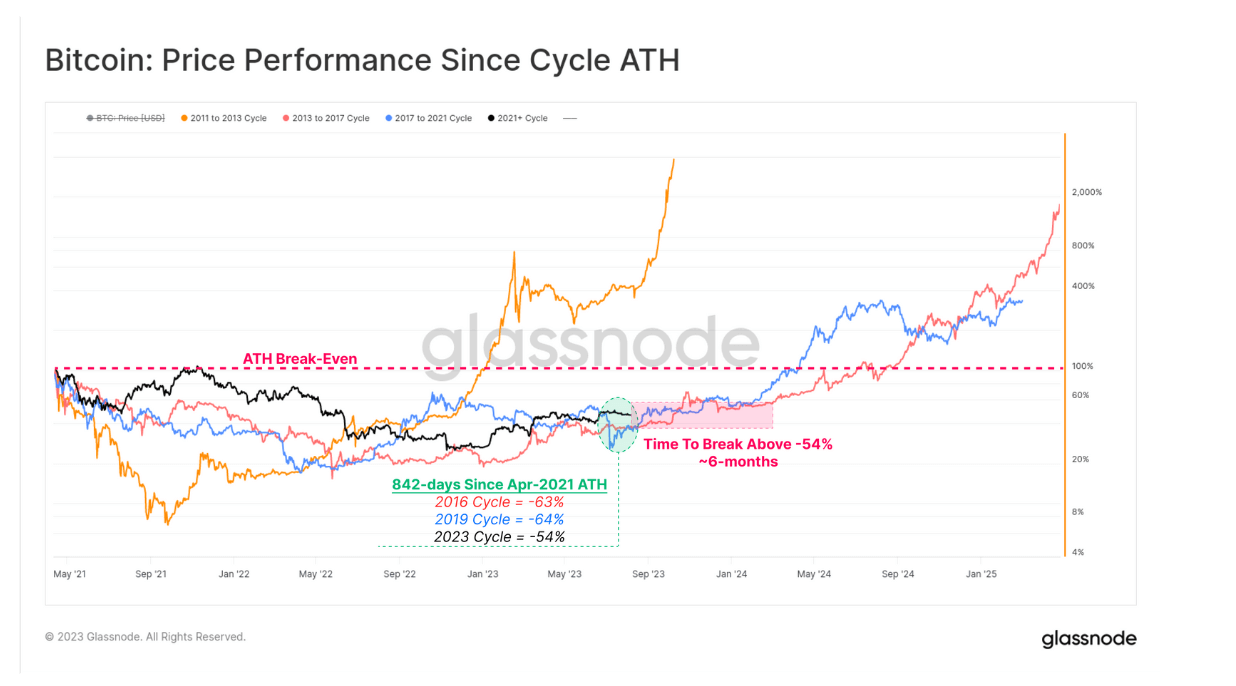
A notable lack of volatility marks Bitcoin’s current cycle, as the leading cryptocurrency meanders below the $30,000 mark. In this phase, even minor price dips spur expectations of more significant falls, again bringing previous support levels into focus. However, investor optimism seems to emerge when it inches upwards, sparking calls for a breach of the 30k threshold. According to Glassnode data, it has been nearly 842 days since Bitcoin hit its all-time high in April 2021.
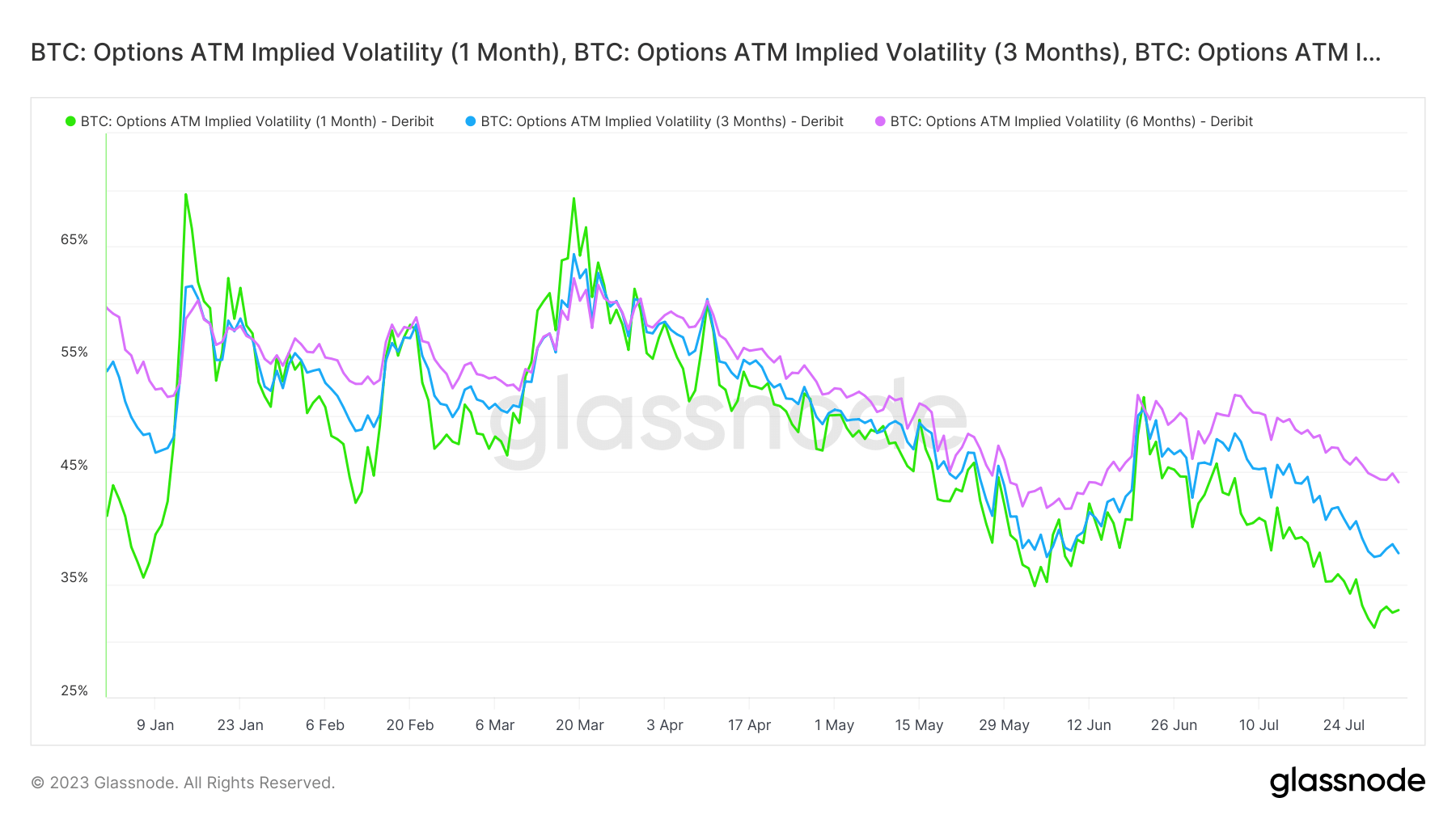
Interestingly, the fact that Bitcoin is trading about 54% below its peak is a notable improvement over previous cycles. This sideways movement, however, could potentially unsettle even the most steadfast investors. Notably, Glassnode identifies that recovery beyond the 54% mark took approximately six months in past cycles, placing us on the doorstep of the next halving event slated for April 2024. Furthermore, Bitcoin’s realized and implied volatility metrics continue to edge toward record lows, mirroring levels unseen since 2016/2017. Realized volatility, reflecting past price changes, stands at 35%, while the anticipatory measure of implied volatility has dipped to 30%, a new low.